Introduction
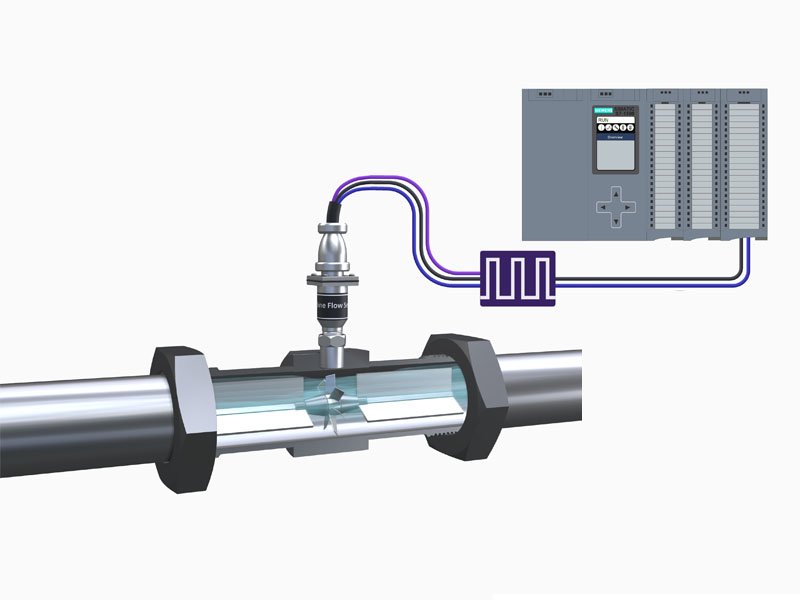
Turbine Flow Meter is inserted in a pipe directly in the flow path.
The mechanical part of the Turbine Flow Meter has a turbine rotor placed in the path of a flowing stream.
The only moving part of the Turbine Meter is the mechanical rotor. The rotational speed of the rotor depends upon the flow velocity. The rotor blades are usually made of stainless steel.
As the rotor spins, the passage of each rotor blade past a pickup point will generate an electrical pulse.
The electrical pulses are created in different ways depending upon the rotor blades themselves and the pickup unit characteristics.

Key Advantages
- Accuracy: Turbine flow meters provide accurate and repeatable flow measurements over a wide range of flow rates.
- Wide Range of Fluids: They can measure a variety of fluids, including water, oils, chemicals, and some gases, depending on the design and materials used.
- Good Turndown Ratio: They can handle a broad range of flow rates, making them versatile for different applications.
Considerations
- Moving Parts: Turbine flow meters have moving parts (the turbine and bearings), which can lead to wear and may require maintenance over time.
- Flow Profile: For accurate measurements, the flow profile should be relatively stable and fully developed before reaching the turbine. Straight pipe sections before and after the meter help achieve this.
- Fluid Characteristics: The fluid should be relatively clean and free from debris or particulates that could damage the turbine or affect measurement accuracy.
In summary, a turbine flow meter works by using a turbine that spins as the fluid flows over its blades. The rotational speed of the turbine, detected by sensors, is converted into a flow rate measurement, providing accurate and reliable flow data for various applications.
