Introduction
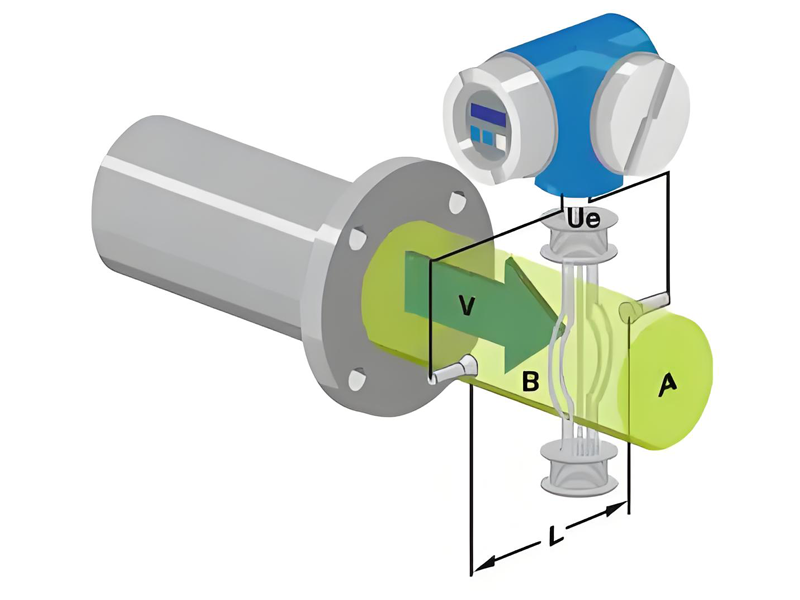
Electromagnetic flow meter, also known as a magmeter, operates based on Faraday’s Law of Electromagnetic Induction.
As the conductive fluid moves through the magnetic field, an electromotive force (EMF) is induced in the fluid. Faraday’s Law states that the voltage induced is proportional to the flow velocity of the fluid, mathematically defined as E=k*B*D*V. The faster the fluid flows, the higher the voltage induced. This voltage is generated due to the interaction of the fluid’s motion and the magnetic field.

